- [자격증][실기] 빅데이터 분석기사 2024년 1회(8회)실기 합격 후기 20 Aug 2024
- [자격증][실기] 정보처리기사 2024년 1회 실기 합격 후기 06 Aug 2024
- [자격증][필기] 빅데이터 분석기사 8회 필기 분석 및 후기 03 May 2024
- [깃허브 블로그]지킬 블로그 카테고리 / SIDEBAR 기능 추가(clean blog theme) 08 Feb 2024
- [깃허브 블로그] 동일 카테고리의 최근 글 기능 개발(clean blog theme) 17 Jan 2024
- [깃허브 블로그]지킬 블로그 카테고리 / NAVBAR 기능 추가(clean blog theme) - 1 15 Dec 2023
- [데이터]개인정보 처리 위탁과 제 3자 제공의 차이 19 Mar 2024
- [AI 그림]프롬프트의 한계점 - 올바른 프롬프트 작성하기 28 Dec 2023
- [데이터 분석]조합에 따른 승률은 얼마나 차이가 날까? 19 Dec 2023
- [AI 그림]프롬프트의 한계점 - 올바른 프롬프트 작성하기 28 Dec 2023
- [Android Studio]Bottom Navigation Bar 구현 - OnItemSelectedListener 이용 29 Dec 2023
- [CS] 2의 보수 02 Jan 2024
- [WEB][JAVA] 개발자 취업 후기 29 Mar 2025
- [WEB][JAVA] JPA 상속 및 심화 28 Dec 2024
- [WEB][Spring] 스프링으로 Chat-GPT 페이지 구현하기 - 2 24 Oct 2024
- [WEB][JAVA] 개발자 취업 후기 29 Mar 2025
- [WEB][REVIEW] 커서 IDE 롱텀 리뷰- AI 에이전트라고 할 만 한가? 29 Mar 2025
- [WEB][JAVA] JPA 상속 및 심화 28 Dec 2024
- [백준][JAVA] 백준 7562번 :: 나이트의 이동 :: 실버 1 02 May 2024
- [백준][JAVA] 백준 12100번 :: 2048(Easy) :: 골드 2 28 Mar 2024
- [백준] 백준 1743번 :: 음식물 피하기 :: 실버 1 27 Feb 2024
- [프로그래머스][PS] 타겟 넘버 :: LEVEL 2 (DP 풀이) 16 Jan 2024
- [백준] 백준 1743번 :: 음식물 피하기 :: 실버 1 27 Feb 2024
- [백준] 백준 1931번 :: 회의실 배정 :: 실버 1 01 Feb 2024
- [백준][자료구조] 백준 2178번 :: 미로 탐색 :: 실버 1 30 Jan 2024
- [프로그래머스][PS] 타겟 넘버 :: LEVEL 2 (DP 풀이) 16 Jan 2024
- [백준][JAVA] 백준 7562번 :: 나이트의 이동 :: 실버 1 02 May 2024
- [백준][JAVA] 백준 12100번 :: 2048(Easy) :: 골드 2 28 Mar 2024
- [백준] 백준 1743번 :: 음식물 피하기 :: 실버 1 27 Feb 2024
- [백준][자료구조] 백준 2178번 :: 미로 탐색 :: 실버 1 30 Jan 2024
- [백준][자료구조] 백준 1935번 :: 후위 표기식 2 :: 실버 3 23 Jan 2024
- [백준][PS] 회사에 있는 사람 :: 실버 5(자료구조) 17 Jan 2024
- [리눅스] 애플 실리콘 맥에 리눅스 설치하는 법(UTM) 01 Feb 2024
- [DB] 구체화된 뷰는 테이블과 어떻게 다를까? 29 Feb 2024
- [후기] 이카운트 코딩 테스트 및 인터뷰 리뷰 11 Dec 2024
- [후기] 웹 개발자의 Cursor AI 사용기 02 Nov 2024
- [후기] 알리익스프레스 SD카드 배송 후기 / 용량 뻥튀기 확인하는법 06 Mar 2024
- [WEB][react] Chat-gpt realtime api 구현 및 설명 15 Oct 2024
- [WEB][REVIEW] 커서 IDE 롱텀 리뷰- AI 에이전트라고 할 만 한가? 29 Mar 2025
TENSOR STUDIO
[백준][JAVA] 백준 12100번 :: 2048(Easy) :: 골드 2
문제 설명
2048 게임은 4×4 크기의 보드에서 혼자 즐기는 재미있는 게임이다. 이 링크를 누르면 게임을 해볼 수 있다.
이 게임에서 한 번의 이동은 보드 위에 있는 전체 블록을 상하좌우 네 방향 중 하나로 이동시키는 것이다. 이때, 같은 값을 갖는 두 블록이 충돌하면 두 블록은 하나로 합쳐지게 된다. 한 번의 이동에서 이미 합쳐진 블록은 또 다른 블록과 다시 합쳐질 수 없다. (실제 게임에서는 이동을 한 번 할 때마다 블록이 추가되지만, 이 문제에서 블록이 추가되는 경우는 없다)
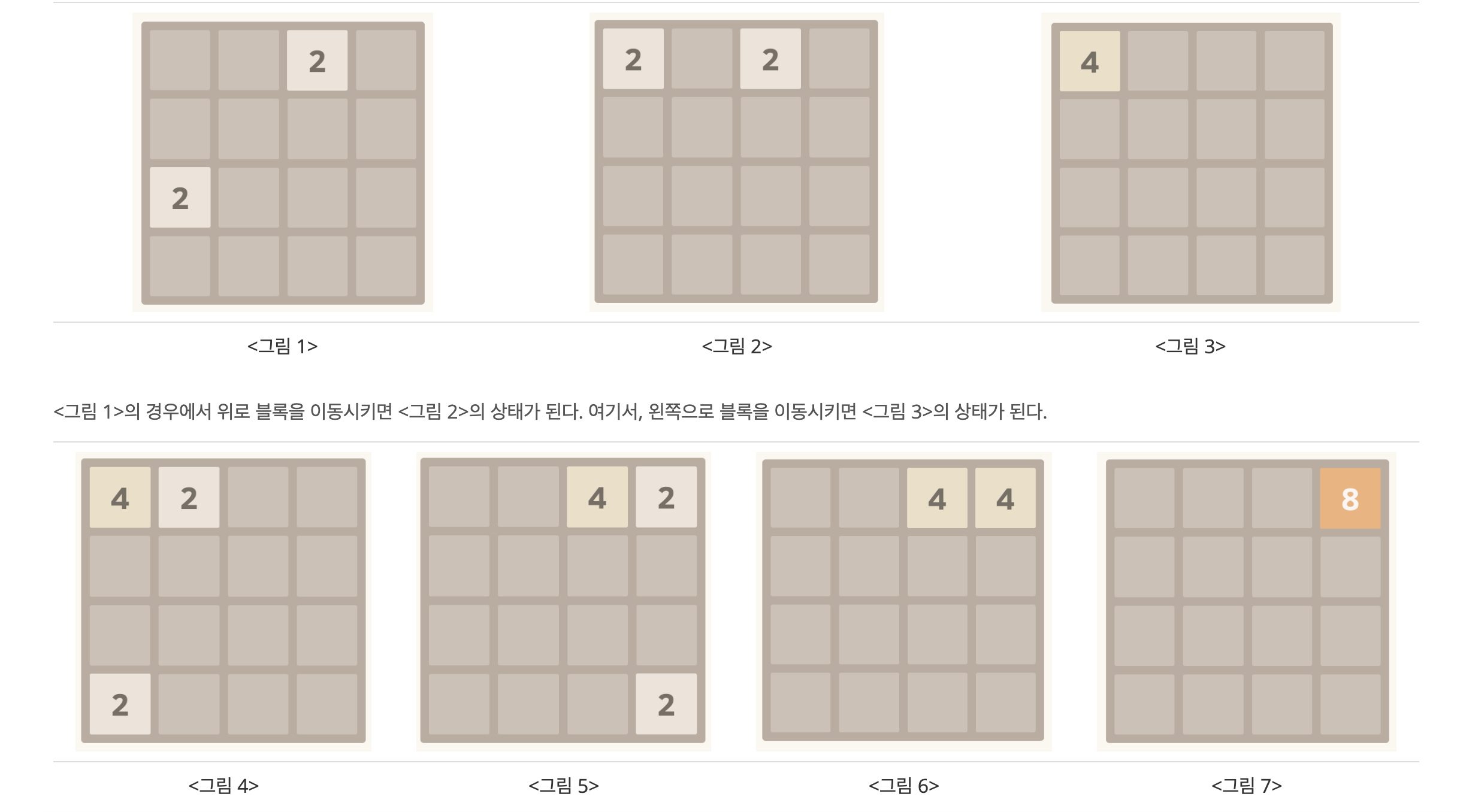
마지막으로, 똑같은 수가 세 개가 있는 경우에는 이동하려고 하는 쪽의 칸이 먼저 합쳐진다. 예를 들어, 위로 이동시키는 경우에는 위쪽에 있는 블록이 먼저 합쳐지게 된다. <그림 14>의 경우에 위로 이동하면 <그림 15>를 만든다.
이 문제에서 다루는 2048 게임은 보드의 크기가 N×N 이다. 보드의 크기와 보드판의 블록 상태가 주어졌을 때, 최대 5번 이동해서 만들 수 있는 가장 큰 블록의 값을 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
문제 입력
첫째 줄에 보드의 크기 N (1 ≤ N ≤ 20)이 주어진다. 둘째 줄부터 N개의 줄에는 게임판의 초기 상태가 주어진다. 0은 빈 칸을 나타내며, 이외의 값은 모두 블록을 나타낸다. 블록에 쓰여 있는 수는 2보다 크거나 같고, 1024보다 작거나 같은 2의 제곱꼴이다. 블록은 적어도 하나 주어진다.
출력
최대 5번 이동시켜서 얻을 수 있는 가장 큰 블록을 출력한다.
예제 입력
3
2 2 2
4 4 4
8 8 8
예제 출력
16
접근방법
사실 이 문제가 골드 2라고는 생각하지 않는다. 왜냐하면 무식한 구현문제라고 생각하기 때문이다. 개인적으로 생각하기엔, 이 정도 수준의 구현을 해당 언어가 제공하는 다양한 문법을 이용해서 풀 수 있다면(GPT 등을 최소한으로 이용하고) 해당 언어를 어느정도 사용할 수 있다고 말할 수 있다고 말해도 좋다.
문제를 해결하고 다른 사람이 어떻게 접근했는지 살펴봤는데, 나처럼 무식하게 전부 구현해버린 사람은 조금 드문것 같다는 생각이 들었다. 일단 이 문제를 해결하는데 있어서 가장 중요한 것은 보드의 칸(이하 노드라고 설명)의 움직임과 숫자가 병합되는 규칙등을 제대로 구현하는 것이다.
왜냐하면 최대 5번 움직여서 가장 큰 수를 출력하는 것 이라는 조건이 붙어있기는 하지만 단순히 5번 움직이는 것의 중복 조합의 갯수를 구해봐야 고작 4^5 수준의 문제공간이기 때문이다. 이정도는 컴퓨터가 모든 중복조합의 경우를 다 구해버리고도 시간이 충분히 남기 때문에, 결국 올바른 구현이 가장 중요하다.
개인적으로 이 문제는 자바를 이용해서 푸는 것도 좋다고 생각하는데, 해당 문제가 객체지향을 연습하기 좀 좋은 예제라고 생각하기 때문이다.
코드
일단 문제를 node 클래스와, board 클래스로 나누어서 구현했다. node 클래스는 각 노드의 값을 저장하고, 이동하는 함수를 구현했다. 보드는 방향 명령을 내리거나 초기화를 하거나 하는 메소드로 구성되어 있고, 노드 클래스에서는 그 명령을 받아 각 노드의 행동을 구현했다.
노드의 이동을 구현할때, 주의해야 할 점은 예를 들어서 왼쪽 명령을 보드에서 노드에 내린다고 해 보자. 그렇다고 하더라도 실제 노드가 이동하는 것이 아니다. 노드는 가만히 있고 해당 노드의 값만 바뀌는 것이다.
0 0 2 라는 열이 존재할 때 왼쪽 명령을 가장 오른쪽 노드가 받는다고 쳐보자. 그런 경우에는 첫번째로 [0, 2]노드가 [0, 1] 노드의 값을 변경한다. 그리고 [0, 1]의 노드의 leftmove 메소드를 호출한다. 이런 식으로 연쇄적으로 방향 명령이 호출되고 병합되는 방식으로 구현된다.
또한 중요한 점은, 한번의 이동에 하나의 노드는 한 번밖에는 병합되지 않는다는 점이다. 다시말해서
[2, 2, 2, 2] 라는 열이 있다고 할 때, 왼쪽 명령을 받는다고 치자. 그 경우에 올바른 결과는 [4, 4, 0, 0] 이다. 또한 [4, 2, 2] 라는 열이 있다고 할 때, 왼쪽 명령을 받으면 그 경우에 올바른 결과는 [4, 4, 0] 이다.
첫번째까지는 생각하기 쉬워도 두번째 예시는 한번에 생각해내기 어렵다. 단순히 병합된 후에 연쇄적인 left 콜이 없으면 연쇄가 끊기니까 문제가 없을것이라고 생각했는데, 이러한 경우에는 두번째 예시를 만족시키지 못하고 [8, 0, 0] 으로 병합되어버리고 만다. 그래서 이런 경우에는 노드의 concated라는 변수를 이용해서 만약 concated가 true이면 한번만 병합되도록 구현했다.
package boj;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class boj12100 {
static int inputedMaximunNumber = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
ArrayList<node> nodeList = new ArrayList<>();
node[][] inputModel = gameSetter(scanner);
board Board = new board(inputModel);
int allMaxNumber = 0;
ArrayDeque<ArrayList<Integer>> orderList = BFS();
for (ArrayList<Integer> row : orderList) {
for (Integer order : row) {
orderInterpreter(order, Board);
}
int tempMaxNumber = Board.getMaxNumber();
if (allMaxNumber < tempMaxNumber) {
allMaxNumber = tempMaxNumber;
}
Board.resetBoard();
}
System.out.println(allMaxNumber);
}
public static node[][] gameSetter(Scanner scanner) {
int boardSize = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
node[][] tempBoard = new node[boardSize][boardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; i++) {
for (int k = 0; k < boardSize; k++) {
int[] coordinate = {i, k};
int tempValue = scanner.nextInt();
inputedMaximunNumber += tempValue;
node tempNode = new node(tempValue, coordinate, tempBoard);
}
scanner.nextLine();
}
return tempBoard;
}
public static void orderInterpreter(int number, board Board) {
switch (number) {
case 0 :
Board.left();
break;
case 1 :
Board.right();
break;
case 2 :
Board.up();
break;
case 3 :
Board.down();
break;
}
}
public static ArrayDeque<ArrayList<Integer>> BFS() {
int[] problemSpace = {0,1,2,3};
ArrayDeque<ArrayList<Integer>> openList = new ArrayDeque<>();
ArrayDeque<ArrayList<Integer>> closedList = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (int i = 0; i < problemSpace.length; i++) {
int tempNode = problemSpace[i];
ArrayList<Integer> tempArray = new ArrayList<>();
tempArray.add(tempNode);
openList.add(tempArray);
}
while (true) {
if (openList.size() == 0) {
return closedList;
}
else {
ArrayList<Integer> selectedNode = openList.pollFirst();
if (selectedNode.size() == 5) {
closedList.add(selectedNode);
}
else {
for (int i : problemSpace) {
ArrayList<Integer> clonedSelectedNode = new ArrayList<>(selectedNode);
clonedSelectedNode.add(i);
openList.add(clonedSelectedNode);
}
}
}
}
}
}
class node {
node[][] model;
int value;
int[] coordinate;
int initialValue;
boolean concated;
// 생성자임
public node(int value, int[] coordinate, node[][] model) {
this.initialValue = value;
this.model = model;
this.value = value;
this.coordinate = coordinate;
this.model[coordinate[0]][coordinate[1]] = this;
this.concated = false;
}
public void concatedReset() {
this.concated = false;
}
public void reset() {
this.value = this.initialValue;
}
// 그런데 그러면 board를 업데이트해야함
public void leftMove() {
if (leftCheck() == 1){
// 왼쪽으로 갈 수 있으면 왼쪽으로 감
// this.coordinate[0] -= 1; << 이런식으로 직접 노드를 옮겨서는 안 됨.
// value를 좌측으로 옮기고 이 노드의 value는 0이 되어야 함.
// 각 체크의 결과는 1 0 value의 값이 나옴, 1인 경우는 옮길 수 있고, 0인 경우는 못옮김
int temp = this.value;
this.value = 0;
// 이 노드의 값을 0으로 초기화하고
// 좌측이므로
node targetNode = this.model[this.coordinate[0]][this.coordinate[1] - 1];
// 좌측 노드의 값을 이 노드의 값으로 치환함
targetNode.value = temp;
// 그리고 그 노드가 왼쪽 끝까지 가야하기 때문에 연쇄적으로 leftMove콜을 함
targetNode.leftMove();
}
else if (leftCheck() == 0) {
}
else {
// 만약 왼편에 존재하는 노드가 값을 가지고 있는 노드의 경우에는
// << 현재 노드의 값과 같으면 합쳐진다
node targetNode = this.model[this.coordinate[0]][this.coordinate[1] - 1];
// 만약 현재 노드의 값과 같아도 concated flag가 true 면 패스한다
if (!targetNode.concated) {
if (targetNode.value == this.value) {
targetNode.value = targetNode.value * 2;
this.value = 0;
targetNode.concated = true;
// 보니까 한번만 합쳐지는것같음 모든 블록은 한번만
// 합쳐져야하기때문에 합친 후에는 연쇄콜을 하면 안됨
// targetNode.leftMove();
}
}
}
}
public void rightMove() {
// leftMove와 작동방식이 같기 때문에 굳이 주석은 적지 않겠다
if (rightCheck() == 1) {
int temp = this.value;
node targetNode = this.model[this.coordinate[0]][this.coordinate[1] + 1];
targetNode.value = temp;
this.value = 0;
targetNode.rightMove();
} else if (rightCheck() == 0) {}
else {
node targetNode = this.model[this.coordinate[0]][this.coordinate[1] + 1];
if (!targetNode.concated) {
if (targetNode.value == this.value) {
targetNode.value = targetNode.value * 2;
this.value = 0;
targetNode.concated = true;
// targetNode.rightMove();
}
}
}
}
public void upMove() {
if (upCheck() == 1) {
int temp = this.value;
node targetNode = this.model[this.coordinate[0] - 1][this.coordinate[1]];
targetNode.value = temp;
this.value = 0;
targetNode.upMove();
} else if (upCheck() == 0) {}
else {
node targetNode = this.model[this.coordinate[0] - 1][this.coordinate[1]];
if (!targetNode.concated) {
if (targetNode.value == this.value) {
targetNode.value = targetNode.value * 2;
this.value = 0;
targetNode.concated = true;
// targetNode.upMove();
}
}
}
}
public void downMove() {
// downCheck는 0이면 움직일 수 없는 곳, 1이면 움직일 수 있는 곳,
if (downCheck() == 1) {
int temp = this.value;
node targetNode = this.model[this.coordinate[0] + 1][this.coordinate[1]];
targetNode.value = temp;
this.value = 0;
targetNode.downMove();
} else if (downCheck() == 0) {}
// 1도 0도 아닌 정수값인경우
else {
node targetNode = this.model[this.coordinate[0] + 1][this.coordinate[1]];
if (!targetNode.concated) {
if (targetNode.value == this.value) {
targetNode.value = targetNode.value * 2;
this.value = 0;
targetNode.concated = true;
// targetNode.downMove();
}
}
}
}
public int leftCheck() {
int xIndex = this.coordinate[0];
int yIndex = this.coordinate[1];
if (yIndex == 0) {
return 0;
// 0 이면 불가능함
}
else {
if (this.model[xIndex][yIndex - 1].value == 0) {
return 1;
// 1이면 옮길 수 있음
}
else {
return this.model[xIndex][yIndex - 1].value;
// 모두 아닌 경우에는 그 노드의 값을 리턴함
}
}
}
public int rightCheck() {
int xIndex = this.coordinate[0];
int yIndex = this.coordinate[1];
// 문제 공간은 정사각형 형태이고 가장 오른쪽에 위치해 있을 때이고
// length는 index보다 1높게 나오므로 1빼줘야함 ㅇㄱㄹㅇ
if (yIndex == this.model[0].length - 1) {
return 0;
}
else {
if (this.model[xIndex][yIndex + 1].value == 0) {
//오른쪽 노드가 공노드이면
return 1;
}
else {
return this.model[xIndex][yIndex + 1].value;
}
}
}
public int upCheck() {
int xIndex = this.coordinate[0];
int yIndex = this.coordinate[1];
if (xIndex == 0) {
//위로 더 이상 올라갈 수 없으면
return 0;
}
else {
if (this.model[xIndex - 1][yIndex].value == 0) {
return 1;
}
else {
return this.model[xIndex - 1][yIndex].value;
}
}
}
/**
* 아래로 움직일 수 있는지 아닌지를 검사하는 함수임
*
* @return 아래로 움직일 수 있으면 0, 아래로 움직일 수 없으면 1, 다른 값이면 해당 노드의 값을 리턴
*/
public int downCheck() {
int xIndex = this.coordinate[0];
int yIndex = this.coordinate[1];
if (xIndex == this.model[0].length - 1) {
//아래로 더 이상 내려갈 수 없으면
return 0;
}
else {
if (this.model[xIndex + 1][yIndex].value == 0) {
return 1;
}
else {
return this.model[xIndex + 1][yIndex].value;
}
}
}
}
class board {
node[][] model;
public board(node[][] inputModel) {
//정사각형이니까
this.model = inputModel;
}
public void resetBoard() {
for (node[] nodes : model) {
for (node x : nodes) {
x.reset();
}
}
}
public void printBoard() {
for (node[] x : model) {
for (node y : x) {
System.out.printf("%d ", y.value);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public int getMaxNumber() {
int maxNumber = 0;
for (node[] x : model) {
for (node y : x) {
if (y.value > maxNumber) {
maxNumber = y.value;
}
}
}
return maxNumber;
}
public void setModel(node[][] model) {
this.model = model;
}
public node[][] getModel() {
return model;
}
/**
* 모든 노드에 대해서 왼쪽 명령을 내림
*/
public void left() {
// 모든 노드에 대해서 왼쪽 노드로 이동
for (node[] x : model) {
for (node y : x) {
y.leftMove();
}
}
// 한번 움직임이 끝났으면 concated 플래그를 다시 reset 해야함
for (node[] x : model) {
for (node y : x) {
y.concatedReset();
}
}
}
public void right() {
// 모든 노드에 대해서 오른쪽 노드로 이동
// for (node[] x : model) {
// for (node y : x) {
// y.rightMove();
// }
// }
// 근데 위의 left식으로 구현하면 안 됨, 왜냐하면 가장 오른편부터 합쳐져야 하기 때문임
int max = model.length - 1;
for (node[] x : model) {
for (int i = max; i >= 0; i--) {
x[i].rightMove();
}
}
for (node[] x : model) {
for (node y : x) {
y.concatedReset();
}
}
}
public void up() {
for (node[] x : model) {
for (node y : x) {
y.upMove();
}
}
for (node[] x : model) {
for (node y : x) {
y.concatedReset();
}
}
}
public void down() {
// for (node[] x : model) {
// for (node y : x) {
// y.downMove();
// }
// }
// 근데 위의 down 식으로 구현하면 안 됨, 왜냐하면 가장 아래쪽부터 합쳐져야 하기 때문임니당
int max = model.length - 1;
for (int i = max; i >= 0; i--) {
node[] targetRow = model[i];
for (node x : targetRow) {
x.downMove();
}
}
for (node[] x : model) {
for (node y : x) {
y.concatedReset();
}
}
}
}
-
[WEB][JAVA] 개발자 취업 후기 29 Mar 2025
-
[WEB][JAVA] JPA 상속 및 심화 28 Dec 2024
-
[WEB][Spring] 스프링으로 Chat-GPT 페이지 구현하기 - 2 24 Oct 2024
-
[WEB][Spring] 스프링으로 Chat-GPT 기능 구현하기 - 1 30 Sep 2024
-
[WEB][Spring] 스프링 N + 1 문제 26 Aug 2024